Socialism has become a buzzword in United States political discourse in recent years. Talks of socialism in the U.S. really began to gain traction when Senator Bernie Sanders threw his hat in the 2016 presidential election on a platform of integrating socialist policies into American government. In response, many of his political opponents and media outlets began to use the term pejoratively to describe any policy that emphasizes collective action or redistribution of wealth. Consequently, Pew Research Center found that 55 percent of Americans had a negative impression of the term “socialism” as of 2019. However, this simplistic view of socialism fails to capture the complexity and nuances of this ideology. I argue that socialism has the potential to address many of the social and economic problems facing the United States today.
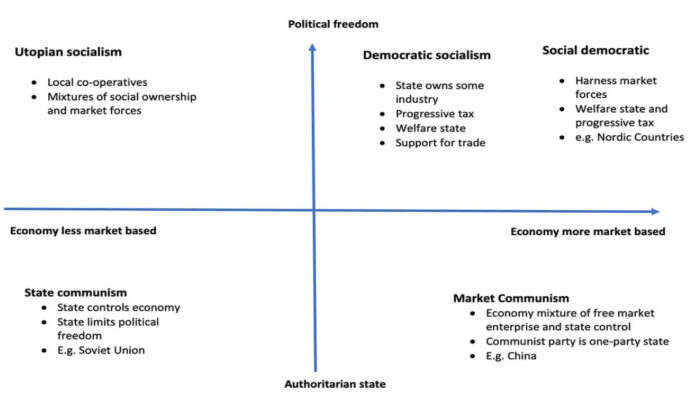
First, it is important to understand what socialism is and what it is not. The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy argues that socialism is “best defined in contrast with capitalism, as socialism has arisen both as a critical challenge to capitalism, and as a proposal for overcoming and replacing it.” At its core, socialism is an economic and political system that emphasizes the collective ownership of the means of production and distribution of goods and services. This means that instead of private individuals or corporations owning factories, land and other resources necessary for production, they are collectively owned and managed by the community of working class citizens or the state. Socialism also emphasizes the idea of social justice and equality, advocating for the redistribution of wealth and resources to ensure that everyone has access to the basic necessities of life, such as healthcare, education and housing.
Contrary to what many opponents of socialism argue, socialism does not necessarily mean a complete eradication of private property or a state-run economy. Rather, socialism can take many different forms, ranging from democratic socialism—which advocates for a mixed economy with a balance between public and private ownership—to market socialism, which proposes a market economy with social ownership of the means of production.
One of the main arguments against socialism in the United States is that it goes against the principles of individualism and free-market capitalism, which have been ingrained in American culture and politics. However, it is important to note that these principles have not always been dominant in the United States. Throughout its history, the country has experimented with various forms of economic systems, from agrarian socialism in the early 19th century to the New Deal programs of the 1930s, which implemented policies such as Social Security, unemployment benefits and minimum wage laws.
Furthermore, many of the social and economic problems facing the United States today—such as income inequality, healthcare disparities and climate change—cannot be adequately addressed by individualistic, market-based solutions alone. These problems require collective action and government intervention to ensure that everyone has access to the resources and opportunities they need to thrive. For example, a socialist healthcare system could provide universal coverage for all Americans, regardless of their income or employment status, while also reducing the cost of healthcare overall by eliminating the profit motive of private insurance companies.
Another benefit of socialism is that it can help address systemic racism and other forms of oppression. In a capitalist system, wealth and power are often concentrated in the hands of a few, perpetuating systemic inequalities based on race, gender and other factors. By contrast, socialism emphasizes the idea of collective ownership and decision-making, which can help empower marginalized communities and promote greater social and economic equality.
Of course, socialism is not the end-all-be-all solution to the problems plaguing the U.S., and there are legitimate concerns about how it would be implemented in practice. Some worry that a socialist system could lead to government overreach and a loss of individual freedom, while others argue that it could stifle innovation and entrepreneurship. These concerns should be taken seriously and addressed through careful planning and implementation of socialist policies.
In conclusion, socialism offers a promising alternative to the individualistic, market-based approach that has dominated American politics for the past few decades. By emphasizing collective ownership, social justice and equality, socialism can help address many of the social and economic problems facing the United States today. While socialism is not without its challenges and drawbacks, it is a worthwhile and necessary conversation for us to have as we work towards building a more just and equitable society.